canine cruciate tear test|canine cruciate ligament injury vet : OEM Diagnosing complete tears of the CrCL is easily accomplished by a veterinarian using a combination of gait observations, physical examination findings, and radiography (X-rays). By contrast, partial CrCL tears may be more challenging to diagnose and may require visual inspection via arthrotomy, mini-arthrotomy, or arthroscopy to confirm.
Test results indicate that Udel® P-1700 and P-1710 WH6517 are highly resistant to significant changes in its mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties when exposed to both standard .
{plog:ftitle_list}
• Autoclave de uso médico, usada para esterilizar instrumental y otros dispositivos sanitarios.• Autoclave de laboratorio, usada para esterilizar material de laboratorio. See more
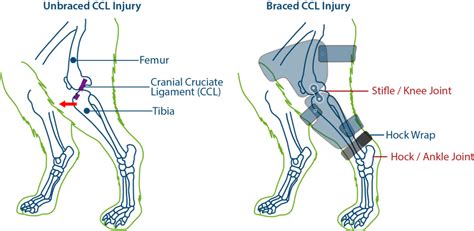
Diagnosing complete tears of the CrCL is easily accomplished by a veterinarian using a combination of gait observations, physical examination findings, and radiography (X-rays). By contrast, partial CrCL tears may be more challenging .In dogs, the most common knee injury is a rupture or tear of the cranial cruciate ligament. Humans have a similar anatomical structure to the dog's knee, but the ligaments are called the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments. Cranial cruciate ligament (CCL) tears are one of the most prevalent orthopedic issues affecting dogs, akin to the ACL injury in humans. This ligament is crucial for stabilizing the knee (or stifle) joint, especially during movement. When a CCL tear occurs, it leads to pain, instability, and difficulty walking, most often resulting in lameness .Specific palpation techniques that veterinarians use to confirm a problem with the CCL are the “cranial drawer test” and the “tibial thrust test.” These tests confirm abnormal motion in the knee and hence a rupture of the CCL.
Value of low-field magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing meniscal tears in the canine stifle: a prospective study evaluating sensitivity and specificity in naturally occurring cranial cruciate ligament deficiency with arthroscopy as the gold standard.
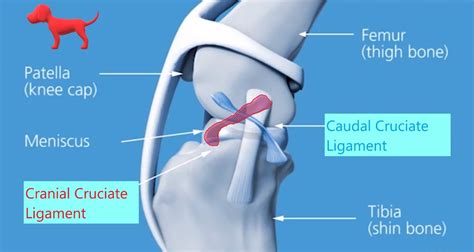
Diagnosing complete tears of the CrCL is easily accomplished by a veterinarian using a combination of gait observations, physical examination findings, and radiography (X-rays). By contrast, partial CrCL tears may be more challenging to diagnose and may require visual inspection via arthrotomy, mini-arthrotomy, or arthroscopy to confirm. The CCL in dogs is analogous to the ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) in people. This ligament connects the femur, the bone in the thigh, to the tibia, or shin bone, in the dog’s hind leg. It is located in the “knee” joint (called the stifle in .
The cranial cruciate ligament (CCL) is a key stabilizing ligament in the knee (or stifle) joint in dogs. It works similarly to the ACL in humans. It works similarly to the ACL in humans. However, unlike humans, CCL injuries in dogs are more often caused by gradual degeneration over time rather than a sudden traumatic event. Canine Cranial Cruciate Ligament Diagram. Finding the Rupture. The ruptured cruciate ligament is the most common knee injury of dogs; in fact, chances are that any dog with sudden rear leg lameness has a ruptured anterior cruciate ligament rather than something else. Cranial Cruciate Ligament Disease (CCLD) is a condition involving the tearing or degeneration of one of the ligaments within your pet's knee joint, known as the cranial cruciate ligament (CCL). 4 min read. If your dog goes lame in one of their hind legs, they may have torn or ruptured their cranial cruciate ligament, or CCL -- similar to the ACL in humans. This ligament connects the.
cruciate ligament rupture treatment for dogs
In dogs, the most common knee injury is a rupture or tear of the cranial cruciate ligament. Humans have a similar anatomical structure to the dog's knee, but the ligaments are called the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments. Cranial cruciate ligament (CCL) tears are one of the most prevalent orthopedic issues affecting dogs, akin to the ACL injury in humans. This ligament is crucial for stabilizing the knee (or stifle) joint, especially during movement. When a CCL tear occurs, it leads to pain, instability, and difficulty walking, most often resulting in lameness .Specific palpation techniques that veterinarians use to confirm a problem with the CCL are the “cranial drawer test” and the “tibial thrust test.” These tests confirm abnormal motion in the knee and hence a rupture of the CCL.
Value of low-field magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing meniscal tears in the canine stifle: a prospective study evaluating sensitivity and specificity in naturally occurring cranial cruciate ligament deficiency with arthroscopy as the gold standard.Diagnosing complete tears of the CrCL is easily accomplished by a veterinarian using a combination of gait observations, physical examination findings, and radiography (X-rays). By contrast, partial CrCL tears may be more challenging to diagnose and may require visual inspection via arthrotomy, mini-arthrotomy, or arthroscopy to confirm. The CCL in dogs is analogous to the ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) in people. This ligament connects the femur, the bone in the thigh, to the tibia, or shin bone, in the dog’s hind leg. It is located in the “knee” joint (called the stifle in .The cranial cruciate ligament (CCL) is a key stabilizing ligament in the knee (or stifle) joint in dogs. It works similarly to the ACL in humans. It works similarly to the ACL in humans. However, unlike humans, CCL injuries in dogs are more often caused by gradual degeneration over time rather than a sudden traumatic event.
Canine Cranial Cruciate Ligament Diagram. Finding the Rupture. The ruptured cruciate ligament is the most common knee injury of dogs; in fact, chances are that any dog with sudden rear leg lameness has a ruptured anterior cruciate ligament rather than something else.
Cranial Cruciate Ligament Disease (CCLD) is a condition involving the tearing or degeneration of one of the ligaments within your pet's knee joint, known as the cranial cruciate ligament (CCL).
itrack pipette tracking system
ivf biopsy pipettes non spiked
cranial cruciate ligament rupture dog
cranial cruciate ligament rupture diagnostic test
El proceso consiste en mantener el material contaminado (previamente lavado y empacado) a una temperatura elevada, por medio del contacto con el vapor de agua bajo presión, durante un período de tiempo .Anotar en el formulario REG-09 “Control Biológico de Autoclaves”, el lote de la ampolla y marcar una cruz al número de registro del equipo autoclave que se está controlando.
canine cruciate tear test|canine cruciate ligament injury vet